In recent years, against the backdrop of a shortage of manpower, FA (factory automation: automation of production processes) and IoT (Internet of Things) in manufacturing sites have been gradually becoming more prevalent.
Collaborative robots that perform tasks such as assembly and inspection instead of humans have also received increasing attention.
Utilizing the bearing technology accumulated over a century, GYJ has developed commodities related to robots in response to market demands.
In this way, GYJ aims to promote the popularization of FA, IoT, and robots, and achieve labor savings and higher efficiency in manufacturing sites.
Wrist Joint Module i-WRIST™
A positioning device that moves as freely as a human wrist
Contributing to labor savings in the manufacturing site
The wrist joint module i-WRIST™ is a module for robots that can perform positioning at high speed.
It achieves free movement similar to that of a human wrist through a special drive mechanism. Moreover, it features a miniaturized design.
By installing an end effector at the front end or combining it with other robots, it can be transformed into various devices.
It is faster, more space-saving, and more labor-saving than before, expanding the possibilities of the manufacturing site.
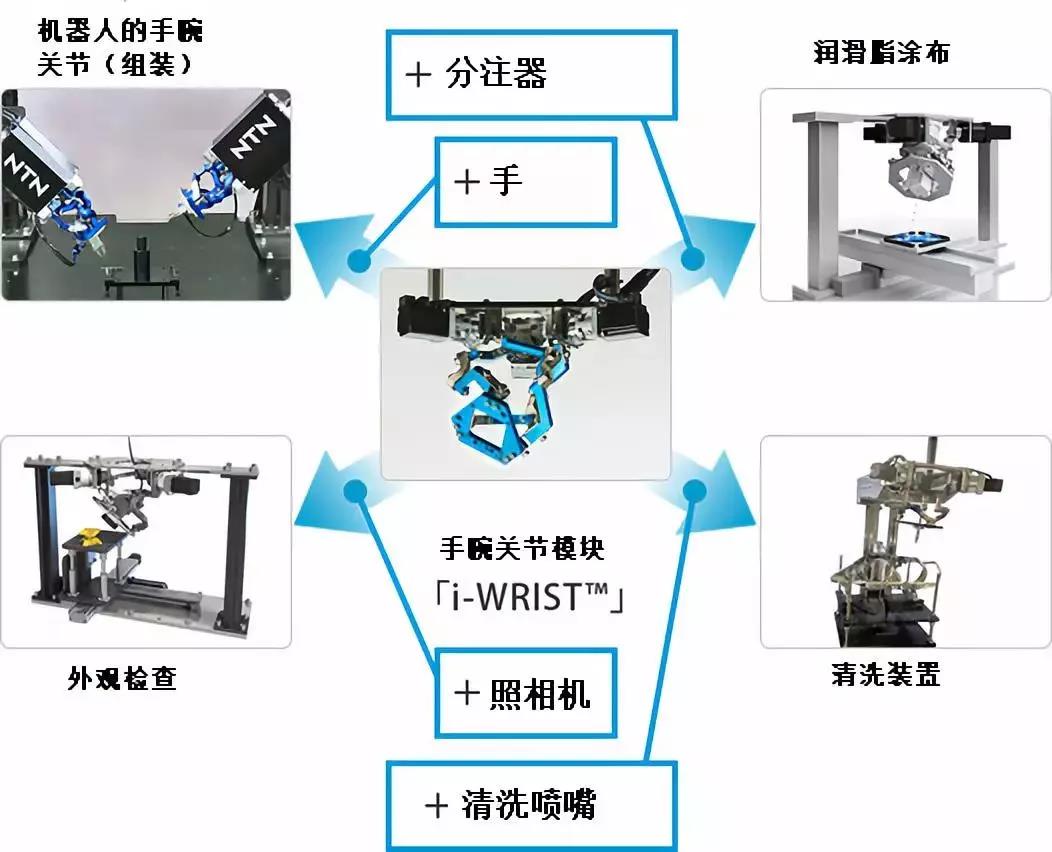
Feature 1 - Wide Range of Motion
With a maximum bending angle of 90° and a rotation angle of 360°, it has a motion range that enables it to quickly lock onto a target at any position on the hemispherical surface. It can rotate countless times in the same direction starting from the target. It can approach the locked position from various angles with the shortest distance.

Feature 2 - High-speed Operation
It can change its posture more than 7 times within 1 second.
It enables high-speed and minute posture changes, which were not the forte of previous robots. It can perform delicate tasks just like a human being at high speed and with precision.
Feature 3 - Compact Design
Thanks to its compact design, it can be easily installed in the limited space of a factory. When combined with the mechanism that rotates the workpiece, it can be set up within the space for manual operation.

i-WRIST™ Derived from Driveshaft Technology
The driveshaft is a product that smoothly transmits the rotation of an automobile engine to the wheels, and it is an essential component for the vehicle's driving and turning.
In the 1960s, GYJ successfully achieved the mass production of driveshafts for the first time in Japan, and now it holds the second-largest market share in the world.
This time, by adopting the driveshaft technology that can transmit rotation smoothly, the i-WRIST™, which can move freely at large angles, has been derived. 
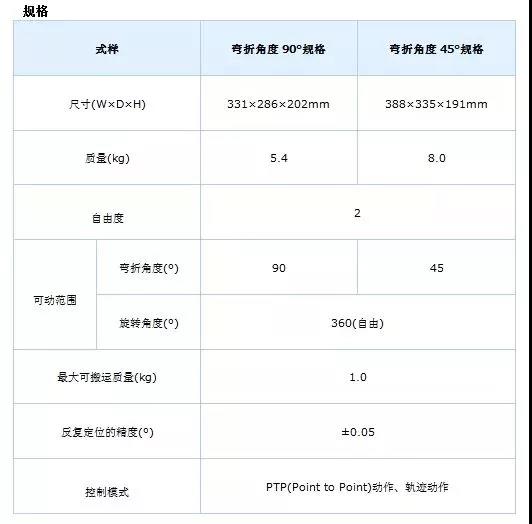
Double-row Magnetic Ring
Detect the absolute angle with high resolution
Enable various robots to achieve delicate and smooth movements
The double-row magnetic ring is a product that bonds a rubber material integrated with magnetic materials and a ring-shaped core.
Combined with a dedicated magnetic sensor, it is used in the joint parts of robots. It can perform fine angle detection of 17 to 20 bits (resolution: approximately 0.0027° to 0.00034°), controlling the robot to achieve delicate movements.
Due to its magnetism, it is not easily affected by vibration, temperature, debris, dust, or oil, and can be used in various environments.
不仅适用于机器人关节部位,也适用于伺服马达等绝对角检测。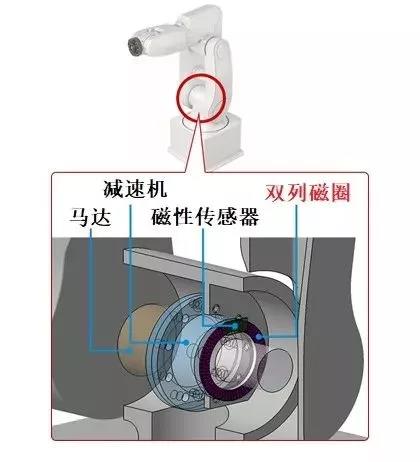
Feature 1 - Special magnetization technology contributes to high-precision angle detection
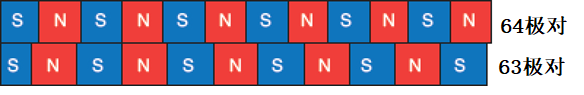
Two rows of magnetic tracks with different numbers of poles (the number of magnetic poles called the N pole or S pole) are formed on the magnetic ring.
When the magnetic ring rotates, a dedicated sensor reads the changes in the magnetic poles of the two rows of magnetic tracks and outputs the absolute angle with high precision through electrical signals.
When performing high-precision angle detection, it is necessary to magnetize the N and S poles at regular intervals and according to the correct rules.
In addition, when the two rows of magnetic rings are formed, a high-precision magnetization technology is required to ensure that the magnetic tracks that are not attracted to each other are not affected.
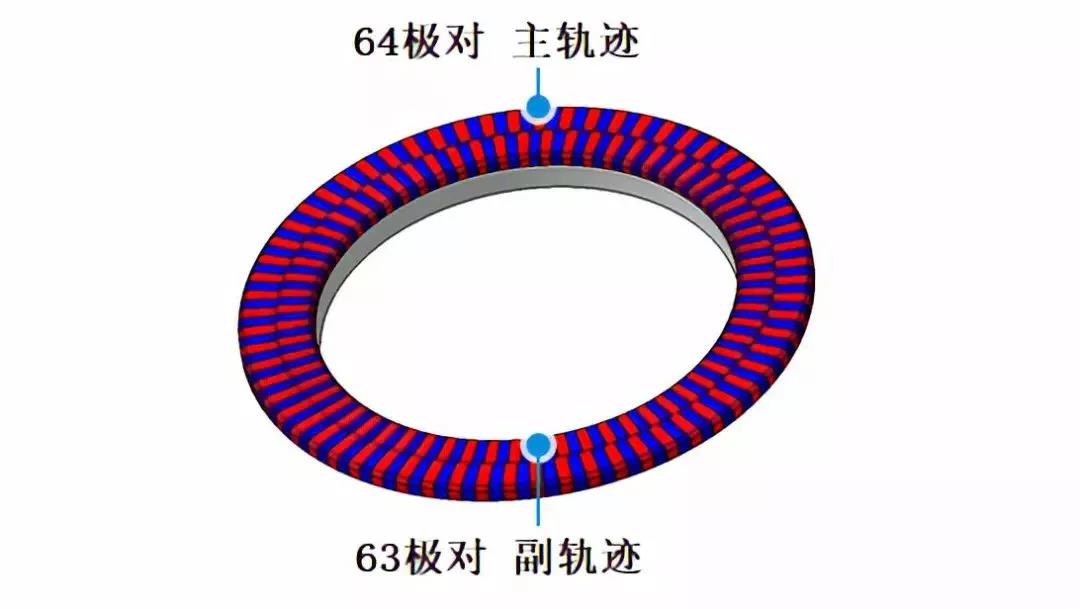
Through the special magnetization technology accumulated through continuous product development, GYJ has successfully achieved high-precision magnetization of 64 pole pairs (paired arrangements of N and S poles) and 63 pole pairs.
Schematic Diagram of the Magnetization Model
High-precision magnetization of 64 pole pairs (paired arrangement of N and S poles) and a double row of 63 pole pairs
Feature 2 - Improving the Design Freedom of Robots
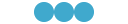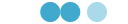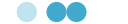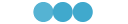
There are currently products in the radial type with a relatively small radial dimension (outer diameter: φ51.5mm) and the axial type with a relatively small width dimension in the axial direction (axial width: 4mm).
Both types have a large diameter and can be installed on a hollow shaft through which cables can pass. By using the structural form suitable for installation, the design freedom is improved, contributing to miniaturization and lightweight.

The Double-row Magnetic Ring Derived from the Bearing with Sensor
The magnetization technology in the double-row magnetic ring is a technology summarized through the development of the bearing with a rotation sensor, which integrates the rotation sensor and the bearing.
The bearing with a rotation sensor is a product used to detect the rotational speed of the motor.
In addition, the hub bearing with a sensor used in the automotive ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) has also been developed. These products are widely used in industrial machinery and automobiles.